



ANIQSpec Integrated Spectroscopy System
ANIQSpec is a Multi-Channel Analyzer spectroscopy system (MCA). A spectroscopy system begins with a detector that outputs voltage pulses. The detector is typically powered with an applied high-voltage, and the signals are sent through an amplifier, which also shapes the pulses. The amplified pulses are fed into an Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC), which generates the digital signal suitable for computer data representation.
The purpose of the MCA is to receive and store this data, and transfer it to the PC memory on command, along with the acquisition time. The board has a 4096-channel memory, where each channel represents a small voltage interval. Each time a pulse is received from the ADC (while the MCA is active), the contents of the appropriate channel is incremented by one. The MCA responds to commands from a software package, which include start/stop data acquisition, transfer data to the PC, and clear the memory of the MCA.
In addition, ANIQSpec comes with a general I/O board to receive signals from thermocouples, RTDs and a variety of sensors, as well as send both analogue and digital control signals to external apparatuses.

The ANIQSpec Integrated Spectroscopy System comprises five components and assorted cables and adapters. These components are:
ANIQVME: VME Backplane Chassis
ANIQ USB-PPI: Interface Module
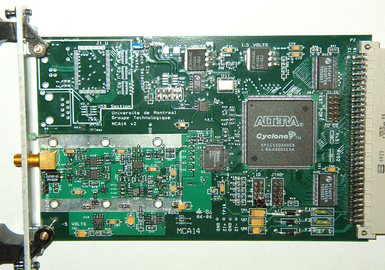
ANIQMCA14: Spectroscopy Module
ANIQHV: High-Voltage Power Supply
ANIQIO: I/O Module & Connection Block
ANIQ USB-PPI: The Interface Module provides the communication between the PC and the VME backplane of the chassis (and hence the other modules). It is either connected to the parallel port by an IEEE-1284 compliant M-M cable, or via a USB connection. Which connection is used is selected by jumper.
ANIQMCA14: The ANIQMCA14 Spectroscopy Module is a combination amplifier, flash ADC and MCA. The user may connect the output of either a NaI detector or a high-resolution Ge detector. This board, like the others in this package, is a half-height unit that fits a VME 3U Slot. One ANIQMCA14 board is required for each detector, and each board has jumpers to set its ID number. This ID number is used by the software, which controls four utterly independent detectors. The operating parameters of the ANIQMCA14 are selected via software, and include the peaking time (for pulse shape analysis), the input polarity, the ADC gain and the LLD.
For Ge detectors, the user may also set the pole zero correction and an additional pulse shaping parameter to compensate for variation in risetime as a function of energy. This gives the MCA14 excellent resolution for Ge detectors, limited only by the detector itself.
ANIQHV: This unit is powered by +12 volts and outputs 1 mA at +1000 volts. It is a highly stable, regulated power supply. The entire interface is on the front panel. The HV output is controlled from 0-1000 volts by a trim potentiometer labelled "Gain", and displayed by a stack of ten LEDs. A DB9 connector is provided to supply power to a standard NaI preamplifier that operates at 12 volts. Other voltages available on request.
ANIQIO: The analog input section of the ANIQIO board may be used to read voltages from thermocouples, RTDs and other devices. There are 16 single-ended channels, which may also be configured in pairs for differential operation. The connection block is also equipped with a temperature sensor for cold junction compensation. Up to eight four-wire RTDs may be connected, and their output voltages are independent of the number of RTDs or the length of their lead wires. There are also five 12-bit analog output channels, and eight digital IO channels, which operate in TTL or Switch mode. Each board has jumpers to set its ID number, used by software to control four utterly independent boards.
ANIQMCA is designed to acquire spectral data in single periods, and display the spectrum in graphical mode. It controls and downloads data from the ANIQSpec Spectroscopy Modules. ANIQMCA allows the user to open a number of documents, limited only by the memory of the PC. Each document is a histogram with an array size of either 1024, 2048 or 4096 channels. Each channel contains an integer from 0 to 232.
The user may create on-line documents, one for each board. Such documents may be used to acquire live data. Since the ANIQSpec boards acquire data independently, acquired data may be recovered when ANIQMCA is started. The data may be saved on disk in an MCA file, which may be read as an off-line document and analysed.
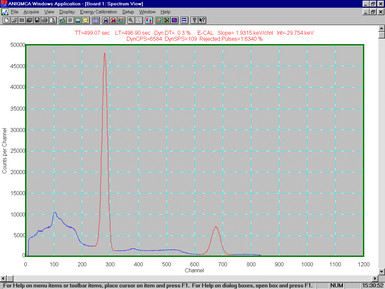
The data may be viewed graphically in the Spectrum View. There is a header that displays the True Time (TT), Live Time (LT) and percentage Dead Time (DT). If an energy calibration is in effect, the slope and intercept are also displayed.
The number of counts is autoscaled, but this may also be modified with the PageUp, PageDown and Home keys. The range may also be manually or automatically scaled, and there is a Zoom feature to view close-ups temporarily. The user may set up to ten Regions-of-Interest (ROIs) on the spectrum, used both to calibrate the energy, and to perform analysis of a photopeak contained therein.
The Data View displays a table of the raw data, with columns for Channel Number, Energy and Counts, as well as ROI data.The Data View displays a table of the raw data, with columns for Channel Number, Energy and Counts, as well as ROI data.
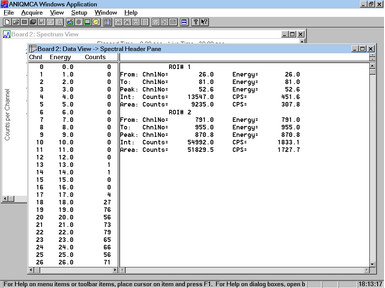
ANIQMCA is also used to define, save and transmit certain parameters to the ANIQSpec Spectroscopy Modules. The parameters are sent to the board's memory, and control how the input voltage pulses are analysed.
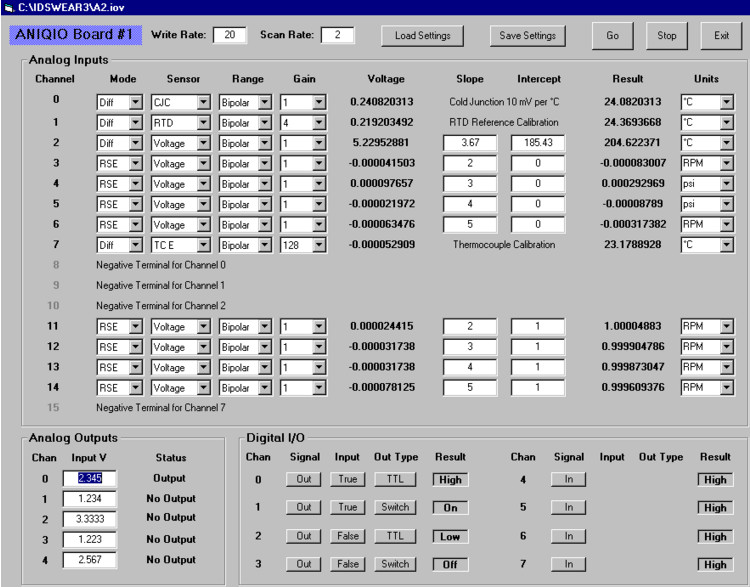
IOViewer is a general control, display and recording software for use with the ANIQIO board. Multiple instances of IOViewer may be called, one for each ANIQIO board present. A file with extension IOV is used to record the settings of the various I/O channels, as well as record the results of the periodic scan of the ANIQIO board attached.
The analog inputs are processed according to a set of input parameters. The "Mode" determines whether the inputs are to be configured as Referenced Single-Ended (RSE) or Differential (Diff). In the RSE mode, any channel's input voltage may be measured with respect to a common ground. In Diff mode, the input to Channels 0 to 7 may be measured with respect to Channels 8 to 15, respectively. The "Sensor" parameters determines which type of sensor is being used for that channel, be it a simple voltage signal, an RTD or one of five types of thermocouples. The voltage read from the board is displayed, as is a result based on a calibration. For thermocouples and RTDs, the calibrations are internal to IOViewer, and the result is in terms of temperature. For simple voltage signals, the user may enter a linear calibration and give a name to the units.
The user may output a voltage via one of five AO channels. Within IOViewer, one merely enters the voltage in the box, and hit return. The appropriate voltage is output.
For each of eight digital I/O channels, the user first selects the "Signal", be it input or output. If output is selected, the user may select the "Out Type" for that channel, be it TTL or switch, and the desired results, either TRUE or FALSE. If "Out Type" is TTL, TRUE sends a 3.3 volt level, otherwise a zero volt level. If "Out Type" is Switch, TRUE turns on the switch, false turns it off. For both Output and Input, the result is shown at each scan.